Aditya-L1: After Moon, ISRO Now Sets Eye On Sun | 10 Facts
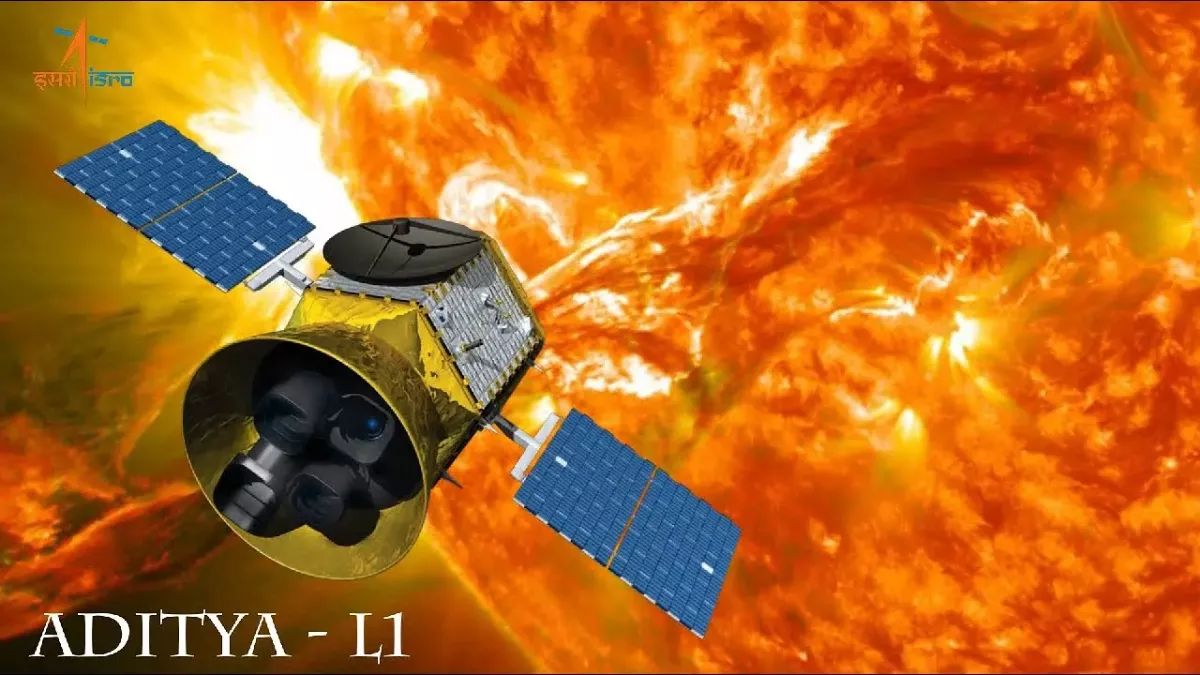
Aditya-L1 aims to provide unprecedented insights into the Sun’s behaviour by placing itself in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, approximately 1.5 million kilometres from Earth.
After the landmark moon mission Chandrayaan-3, ISRO is now shifting the focus to its next space odyssey which is India’s maiden solar mission Aditya-L1, which is ready and will be launched in the first week of September. “Aditya L1 satellite is ready. It has reached Sriharikota and is connected to PSLV. The next aim of ISRO and the country is its launch. The launch will be in the first week of September. The date will be announced within two days,” ISRO chief said.
“After the launch, it will go to an elliptical orbit and from that it will travel to the L1 point which will almost take 120 days,” he added.
Here, Check 10 Facts To Know About India’s Sun Mission:
-Aditya-L1 is the first space-based Indian observatory to study the Sun.
-Aditya-L1 aims to provide unprecedented insights into the Sun’s behaviour by placing itself in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, approximately 1.5 million kilometres from Earth.
-The mission will extensively study the solar winds, which can cause disturbance on Earth and are commonly seen as “auroras”.
-This strategic location will enable Aditya-L1 to continuously observe the Sun without being hindered by eclipses or occultation, allowing scientists to study solar activities and their impact on space weather in real-time.
-Aditya-L1 spacecraft is equipped with seven advanced payloads designed to scrutinize various layers of the Sun, from the photosphere and chromosphere to the outermost layer, the corona.
-Seven payloads employed will be electromagnetic, particle and magnetic field detectors to capture data crucial for understanding phenomena like coronal heating, coronal mass ejections, solar flares, and more.
-One of the most exciting aspects of Aditya-L1’s mission is its ability to directly view the Sun from its unique vantage point at L1. This will enable four payloads to capture clear observations of the Sun, while the remaining three payloads will conduct in-situ studies of particles and fields at this Lagrange point.
-Aditya-L1’s combined observations promise to unlock the mysteries behind solar dynamics and their effects on the interplanetary medium.
-According to ISRO, after the launch, it will take 120 days for the earth to reach Lagrange point 1 (L1). It will head to a kind of parking lot in space where objects tend to stay put because of balancing gravitational forces, reducing fuel consumption for the spacecraft. Those positions are called Lagrange Points, named after Italian-French mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange.
-Reportedly, Aditya-L1 has been built at a cost of Rs 378 crore in 2019 for the mission to study the Sun’s atmosphere.